The federal Research Support Fund assists Canadian postsecondary institutions with the costs associated with managing their research enterprise, helping them to maintain a world-class research environment.
The objective of the Research Support Fund (RSF) is to assist Canadian postsecondary institutions with the expenses associated with managing the research funded by the three federal research granting agencies (CIHR, NSERC, SSHRC). Research funding provided through the granting agencies is generally limited to direct project costs (e.g., research equipment, research assistant salaries, etc.). Institutions whose researchers receive funding for research also incur costs to manage their research enterprise. These are often called indirect costs of research.
Indirect costs of research are real, ongoing, necessary operating expenses that cannot be wholly attributed to any one department, project or product. They include elements such as: building and facility operating costs including heating, cooling, power, cleaning, maintenance; Faculty and departmental services such as machine and electrical shops, grant facilitation, secretarial and office assistance, purchasing, shared equipment, etc.; academic services such as the Library and Computing Service; university-provided administrative services such as Purchasing, Finance, and Human Resources; and research and contract administration & support such as Office of Research Services, University-Industry Liaison Office, Research & Trust Accounting, CFI Office, Health Research Office, Hospital Research Institute Administrations, etc.
RSF funds may be used to cover new expenditures, to maintain the current level of services, or to support an institution's research environment and improve its management. The five expenditure areas are:
- Research facilities;
- Research resources;
- Management and administration of an institution's research enterprise;
- Regulatory requirements and accreditation; and
- Intellectual property and knowledge mobilization.
Overall, grants for indirect costs must add to, and not displace, any research support funds that postsecondary institutions have received from the provincial government, private sector or other federal sources.
Whether the grant pays for the maintenance of libraries, laboratories or research networking spaces, or for the technical support required for an institution's website or library computer system, the overall goal of the fund is to help ensure Canada's research institutions remain among the best in the world. By subsidizing the financial burden of indirect costs, the fund ultimately helps researchers and universities focus on delivering innovative research and scholarly excellence.
The Incremental Project Grants (IPG) funding opportunity is a new stream of the Research Support Fund (RSF), in addition to the RSF grant, that provides further support for the indirect costs of research.
The IPG will provide eligible institutions with additional support for projects that focus on a set of priorities that cut across the RSF’s five existing categories of eligible expenses. The initial four IPG priority areas are:
- innovation and commercialization activities;
- facilities renewal, including deferred maintenance;
- information resources, including digital resources, open access and databases; and
- equity, diversity and faculty renewal (in the context of equity, diversity and inclusion).
The Government of Canada introduced new funding through the Research Support Fund (RSF) in Budget 2022 to further support the activities related to the indirect costs of research security and to support the National Security Guidelines for Research Partnerships. The investments in research security will provide $125 million over five years, starting in 2022-23, and $25 million ongoing per year, in addition to the existing investments for the RSF and Incremental Grant Projects (IPGs).
Research security is categorized as a fifth priority area of the IPGs. These investments are aligned with the RSF’s objectives to help Canadian postsecondary institutions ensure their federally funded research projects are conducted in world-class facilities with the best equipment and administrative support available. By directing funds to specific investments and to annual or multiyear projects initiated by institutions, research security funding will help to build capacity within postsecondary institutions to identify, assess and mitigate the potential risks to research security.
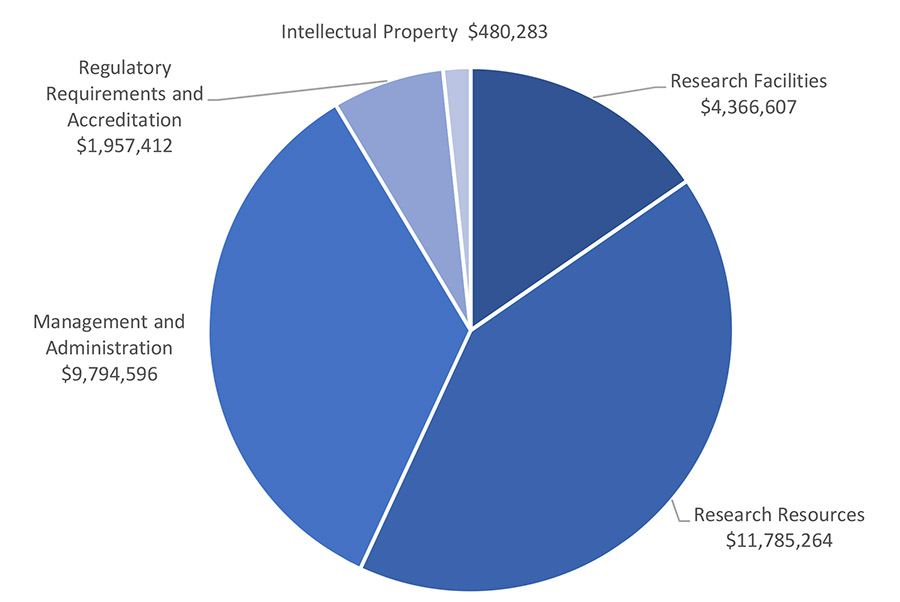
The amount of UBC’s RSF grant is calculated using an algorithm based on the amount of funding awarded in the previous fiscal year by Federal granting agencies. According to this calculation, in 2023/24 UBC's notional allocation is $26,699,857. The expected allocation across the expenditure areas is as follows.
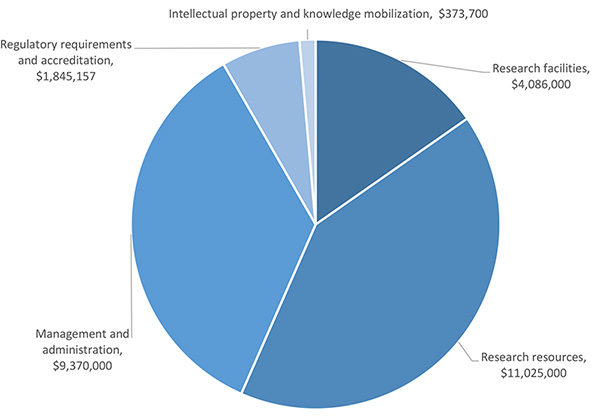
Research Facilities $4,086,000
Research Resources $11,025,000
Management and Administration $9,370,000
Regulatory Requirements and Accreditation $1,845,157
Intellectual Property and Knowledge Mobilization $373,700
A portion of this allocation is retained to support central research administration units and core facilities, and the rest of the allocation is distributed to UBC faculties and affiliated research institutes where eligible costs are incurred.
INCREMENTAL PROJECT GRANT
An additional Incremental Project Grant of $6,043,587 is anticipated in 2023/24.
IPG Project 1: EDI in Research Action Plan: Implementation, Resources and Training
IPG Amount for reporting period: $188,587
Priority Area: Equity, diversity and faculty renewal (In the content of equity, diversity and inclusion)
IPG Project 2: Advanced Research Computing
IPG Amount for reporting period: $4,400,000
Priority Area: Information resources, including digital resources, open access and database
IPG Project 3: Plant Care Services
IPG Amount for reporting period: $475,000
Priority Area: Facilities renewal, including deferred maintenance
IPG Project 4: Global Research Excellence Institutes – BioProducts Institute
IPG Amount for reporting period: $980,000
Priority Area: Innovation and commercialization activities
Research Security
An additional Research Security allocation of $2,357,830 is anticipated in 2023/24.
Security Project 1: Expansion of Research Security Activities
Amount for reporting period: $1,000,000
IPG Priority Area: Research Security
Security Project 1: Enhanced IT Measures
Amount for reporting period: $1,357,830
IPG Priority Area: Research Security
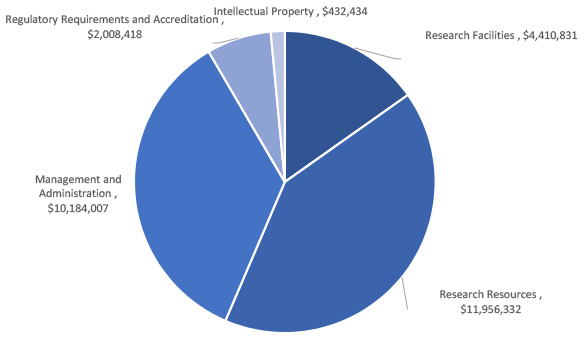
The amount of UBC’s RSF grant is calculated using an algorithm based on the amount of funding awarded in the previous fiscal year by Federal granting agencies. According to this calculation, in 2022/23 UBC's allocation was $27,149,452. The allocation across the expenditure areas was as follows.
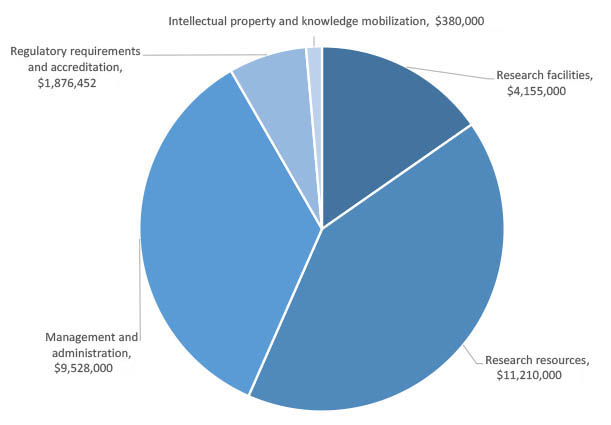
Research Facilities $4,155,000
Research Resources $11,210,000
Management and Administration $9,528,000
Regulatory Requirements and Accreditation $1,876,452
Intellectual Property and Knowledge Mobilization $380,000
A portion of this allocation is retained to support central research administration units and core facilities, and the rest of the allocation is distributed to UBC faculties and affiliated research institutes where eligible costs are incurred.
INCREMENTAL PROJECT GRANT
An additional Incremental Project Grant of $6,087,373 was received in 2022/23.
IPG Project 1: Improved EDI - Dimensions Pilot Project (extension)
IPG Amount for reporting period: $500,000
Priority Area for reporting period: Equity, diversity and faculty renewal (In the content of equity, diversity and inclusion)
IPG Project 2: Advanced Research Computing
IPG Amount for reporting period: $4,324,373
Priority Area: Information resources, including digital resources, open access and database
IPG Project 3: Plant Care Services
IPG Amount for reporting period: $378,000
Priority Area: Facilities renewal, including deferred maintenance
IPG Project 4: Global Research Excellence Institutes – BioProducts Institute
IPG Amount for reporting period: $885,000
Priority Area: Innovation and commercialization activities
RESEARCH SECURITY
An additional Research Security allocation of $2,368,707 was received in 2022/23.
Security Project 1: Expansion of Research Security Activities
Amount for reporting period: $400,000
IPG Priority Area: Research Security
Security Project 1: Enhanced IT Measures
Amount for reporting period: $1,968,707
IPG Priority Area: Research Security
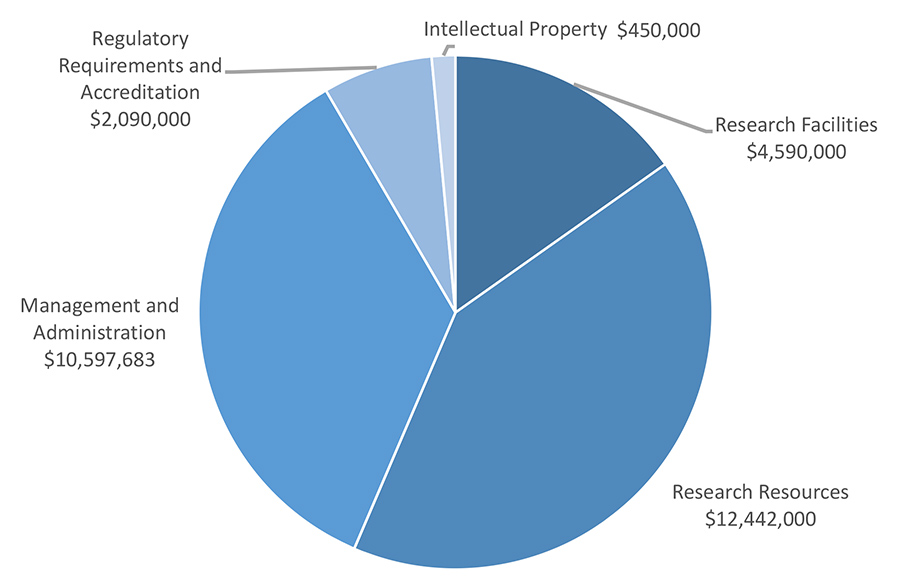
The amount of UBC’s RSF grant is calculated using an algorithm based on the amount of funding awarded in the previous fiscal year by Federal granting agencies. According to this calculation, in 2021/22 UBC's allocation was $27,440,386. The allocation across the expenditure areas was as follows.
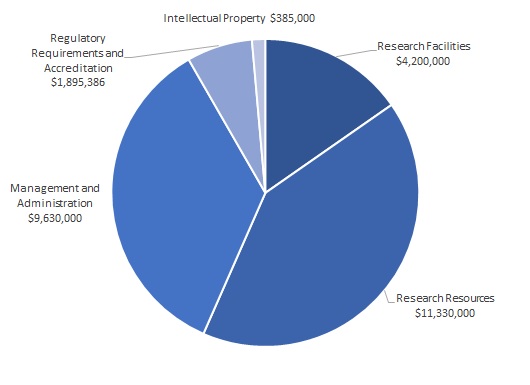
A portion of this allocation is retained to support central research administration units and core facilities, and the rest of the allocation is distributed to UBC faculties and affiliated research institutes where eligible costs are incurred.
INCREMENTAL PROJECT GRANT
An additional Incremental Project Grant of $6,090,968 was received in 2021/22.
IPG Project 1: Improved EDI - Dimensions Pilot Project
IPG Amount for reporting period: $250,000
Priority Area: Equity, diversity and faculty renewal (In the content of equity, diversity and inclusion)
IPG Project 2: Integrated Renewal Program - Workday RISE systems integration
IPG Amount for reporting period: $277,968
Priority Area: Information resources, including digital resources, open access and databases
IPG Project 3: Advanced Research Computing
IPG Amount for reporting period: $4,300,000
Priority Area: Information resources, including digital resources, open access and database
IPG Project 4: Plant Care Services
IPG Amount for reporting period: $378,000
Priority Area: Facilities renewal, including deferred maintenance
IPG Project 5: Global Research Excellence Institutes – BioProducts Institute
IPG Amount for reporting period: $885,000
Priority Area: Innovation and commercialization activities
The amount of UBC’s RSF grant is calculated using an algorithm based on the amount of funding awarded in the previous fiscal year by Federal granting agencies. Using this calculation, in 2020/21 UBC's allocation was $27,825,321. The allocation across the expenditure areas was as follows.
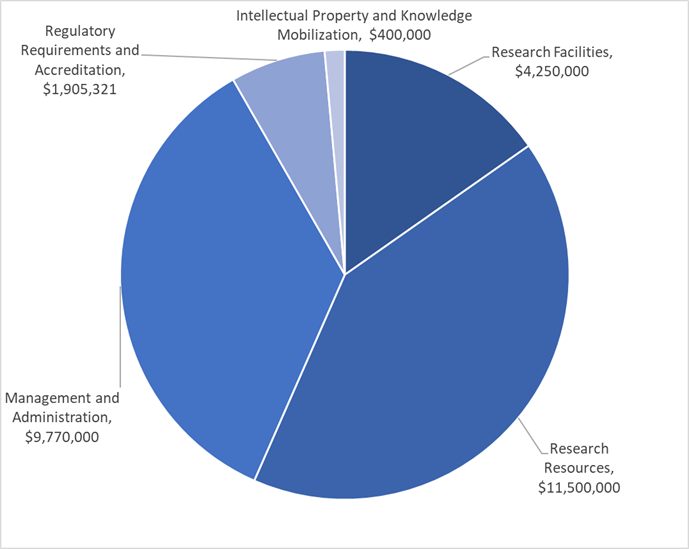
A portion of this allocation is retained to support central research administration units and core facilities, and the rest of the allocation is distributed to UBC faculties and affiliated research institutes where eligible costs are incurred.
INCREMENTAL PROJECT GRANT
An additional Incremental Project Grant of $4,787,194 was received in 2020/21.
IPG Project 1: entrepreneurship @UBC
IPG Amount: $2,895,000
Priority Area: Innovation and commercialization activities & Facilities renewal, including deferred maintenance
IPG Project 2: Innovation UBC
IPG Amount: $1,000,000
Priority Area: Innovation and commercialization activities & Facilities renewal, including deferred maintenance
IPG Project 3: Research Information System Enterprise (RISe)
IPG Amount: $302,000
Priority Area: Information resources, including digital resources, open access and database
IPG Project 4: Improved EDI - Dimensions Pilot Project
IPG Amount: $250,000
Priority Area: Equity, diversity and faculty renewal (in the context of equity, diversity and inclusion)
IPG Project 5: Integrated Renewal Program - Workday RISE systems integration
IPG Amount: $340,194
Priority Area: Facilities renewal, including deferred maintenance & Information resources, including digital resources, open access and databases
A portion of this allocation is retained to support central research administration units and core facilities, and the rest of the allocation is distributed to UBC faculties and affiliated research institutes where eligible costs are incurred.
Incremental Project Grant
An additional $4,060,688 was received through the Incremental Project Grant and allocated as below:
Project: entrepreneurship @UBC
Priority area: A & B (Innovation and commercialization activities & Facilities renewal, including deferred maintenance)
IPG amount for reporting period: $2,946,000
Project: Innovation UBC
Priority area: A & B (Innovation and commercialization activities & Facilities renewal, including deferred maintenance)
IPG amount for reporting period: $836,000
Project: Research Information System Enterprise (RISE)
Priority area: C (Information resources, including digital resources, open access and databases)
IPG amount for reporting period: $278,688
A portion of this allocation is retained to support central research administration units and core facilities, and the rest of the allocation is distributed to UBC faculties and affiliated research institutes where eligible costs are incurred.
INCREMENTAL PROJECT GRANT
An additional $3,112,468 was received through the Incremental Project Grant and allocated as below:
Project: entreprenership @UBC Priority area: A (Innovation and commercialization activities) IPG amount for reporting period: $1,825,000
Project: Innovation UBC Priority area: A & B (Innovation and commercialization activities & Facilities renewal, including deferred maintenance) IPG amount for reporting period: $808,000
Project: Research Information System Enterprise (RISE) Priority area: C (Information resources, including digital resources, open access and databases) IPG amount for reporting period: $479,468
A portion of this allocation is retained to support central research administration units and core facilities, and the rest of the allocation is distributed to UBC faculties and affiliated research institutes where eligible costs are incurred.
The amount of UBC’s RSF grant is calculated using an algorithm based on the amount of funding awarded in the previous fiscal year by Federal granting agencies. Using this calculation, in 2016/17 UBC received a grant of $30,999,045. The expected expenditure across the five categories is shown in the chart.
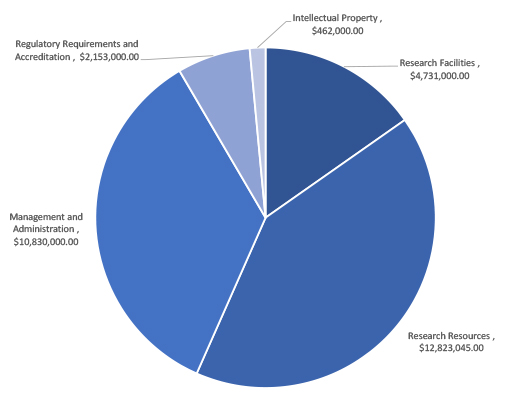
Research Facilities $4,731,000.00
Research Resources $12,823,045.00
Management and Administration $10,830,000.00
Regulatory Requirements and Accreditation $2,153,000.00
Intellectual Property $462,000.00
A portion of this allocation is retained to support central research administration units and core facilities, and the rest of the allocation is distributed to UBC faculties and affiliated research institutes where eligible costs are incurred.
Banff International Research Station
BC Academic Health Science Network
Canadian Institute for Advanced Research
Carey Theological College
Centre for Health Services and Policy Research
First Nations Health Authroity
Fraser Health Authority
Institute of Health Promotion Research
Interior Health Authority
Kinsmen Lab of Neurological Research
Pacific Institute for Climate Solutions
Pacific Institute for the Mathematical Sciences
Providence Health Care
- BC Centre on Substance Use
- Centre for Health Evaluation and Outcome Sciences
- Centre for Healthy Aging at Providence
- Centre for Practitioner Renewal
- UBC James Hogg Research Centre
- Providence Health Research Institute
- Holy Family Hospital
- Mount St. Joseph Hospital
- St. Vincent’s Hospital
- St. Paul’s Hospital
- BC Centre of Excellence for HIV/AIDS
- Canadian HIV Trials Network
Provincial Health Services Authority
- BC Cancer
- BC Cancer Research Center
- Terry Fox Laboratory
- BC Centre for Disease Control
- BC Centre for Excellence for Women’s Health
- BC Children’s Hospital Research Institute (previously Child and Family Research Institute)
- BC Mental Health Society
- BC Mental Health & Addictions Research Institute (BCMHARI)
- BC Provincial Renal Agency
- BC Transplant Society
- Children’s and Women’s Health Centre of BC
- Sunny Hill Health Centre for Children
- Women’s Health Research Institute
- Forensic Psychiatric Services Commission
- Forensic Psychiatric Unit
Regent College
St. Andrew’s Hall
St. Mark’s College
TRIUMF
UBC Okanagan
Vancouver School of Theology
Vancouver Coastal Health Authority
- Vancouver Coastal Health Research Institute
- Community Health Facilities in Powell River, the Sunshine Coast and along the coastal corridor
- Lions Gate Hospital
- Richmond Hospital
- Vancouver Hospital and Health Sciences Centre
- Arthritis Research Centre of Canada
- GF Strong Rehabilitation Centre
- Mary Pack Arthritis Centre
- UBC Hospital
- Vancouver General Hospital
- Jack Bell Research Centre
FACILITIES
Investment in Facilities: $4,086,000
Develop new and maintain existing research facilities.
Amount of shared research platform space
Increase efficiency, capacity and effectiveness of research infrastructure through refreshed governance and utilization models.
RESOURCES
Investment in Resources: $11,025,000
Expand UBC's research computing support by enabling greater access to and utilization of internal and external advanced research computing resources, including research data management.
Utilization of research computing resources by the UBC research community.
Increased user base for research computing resources; Increased utilization of research computing resources; Increased range of services and resources
MANAGEMENT AND ADMINISTRATION
Investment in Management and Administration: $9,370,000
Maintain and improve institutional support for research proposal development and grant/award applications.
Grant application success rate; Total annual grant funding.
Maintain indicator performance levels, focus on increasing service levels to internal and external stakeholders; Improved workflow for grant facilitation and pre-award administration.
REGULATORY REQUIREMENTS AND ACCREDITATION
Investment in Regulatory Requirements and Accreditation: $1,845,157
Implement new opportunities to facilitate meaningful and compliant review of human, animal, chemical, and biosafety research protocols
Improve existing modules in the Research Information Services (RISe) Platform; ensure ongoing compliance of modules with policy and regulation
Enhance data flows between RISe modules and other University platforms to further develop automations for routine processes
INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AND KNOWLEDGE MOBILIZATION
Investment in Intellectual Property and Knowledge Mobilization: $373,700
Through enhanced integration of the governance and operations, continue to provide internationally recognized level of service to researchers and external partners through the University-Industry Liaison Office.
Knowledge mobilization metrics such as patenting, licensing, invention disclosures, spin-off company creation, and industry partnerships created.
Maintain indicator performance levels, focus on increasing service levels to internal and external stakeholders.
EDI in Research Action Plan: Implementation, Resources and Training
Investment in integration and implementation of UBC's EDI in Research Action Plan: $188,587
Priority Area: Equity, diversity and faculty renewal (In the content of equity, diversity and inclusion)
- Integration into UBC's new Strategic Equity and Anti-Racism (StEAR) Framework
- Improved data infrastructure and governance to facilitate the collection and reporting of demographic and experiential data
- Development and provision of training resources
Strategic integration of EDI action plan steps into UBC's StEAR framework, implementation of action plan items, and provision of training resources.
Advanced Research Computing (ARC)
Investment in critical digital research infrastructure, training, resources, open access and databases: $4,400,000
Priority Area: Information resources, including digital resources, open access and databases
- Increased usability and adoption of Cloud services by adding new platforms and services
- UBC systems enhanced to more closely align with Digital Research Alliance Canada systems
- Enhanced efficiencies for researchers accessing the high-performance computing platform by eliminating need for code adjustments
- Expanded training and education by standardizing core offerings, and creating (academic) domain-specific offerings
- New platforms and services added to support researchers’ needs for data analytics and visualization
Enhanced critical digital research infrastructure available to support the UBC research community
Plant Care Services
Investment in facility and service provision: $475,000
Priority Area: Facilities renewal, including deferred maintenance
- Extended irrigation capacity for research fields
- Improved infrastructure in greenhouses to enhance climate control capability
- Refreshed horticultural lighting to enhance capacity in main greenhouse
- Enhanced capacity to provide consultation, advice, and technical support on appropriate scientific methodology and experimental design
Improved services and facilities provided to the UBC community by Plant Care Services
Global Research Excellence Institutes – BioProducts Institute
Investment to support partnerships and research impacts: $980,000
Priority Area: Innovation and commercialization activities
- Continued expansion of the Boreal Alliance
- Start-ups created and launched to enable greater real-world impact of research findings
- Continued diversification of partner research organizations
New partnerships, funding and/or commercialization and knowledge mobilization activities
Expansion of Research Security Activities
Investment in staffing and resources: $1,000,000
IPG Priority Area: Research Security
- Increase in Research Security staff team
- Creation of resource library for scholars and researchers
- Expanded support for risk assessments for other Tri-Agency programs as necessary
Increased support through activities of larger dedicated support team
Enhanced IT Measures
Investment in online resources and cybersecurity infrastructure: $1,357,830
IPG Priority Area: Research Security
- Ongoing subscription to online database for identifying sanctions, security threats, and export controls
- Continued investment to increase capacity to protect researchers and their data from the risk of cyberattacks and breaches. Initiatives could involve platforms to enable multi-factor authentication, device-level encryption, and other tools for incident response.
Enhanced cybersecurity environment for researchers
FACILITIES
Investment in Facilities: $4,155,000
Develop new and maintain existing research facilities.
Amount of significantly renovated research space.
Increase efficiency, capacity and effectiveness of space utilization through reconfiguration of facilities and research spaces.
Status: Objective Met
Over the past year, UBC has upgraded multiple research facilities. The Pacific Centre for Isotopic and Geochemical Research was developed into a shared research platform to serve the scientific community. Upright Open MRI, the only MRI scanner of its kind in the world dedicated to research, underwent a major software upgrade to bring it on par with clinical MRIs. Facility for Infectious Disease and Epidemic Research has also positioned itself as a pandemic-ready facility by providing biosafety and biosecurity training to ensure practices and techniques remain current.
RESOURCES
Investment in Resources: $11,210,000
Expand UBC's advanced research computing (ARC) support by enabling greater access to and utilization of internal and external advanced research computing resources, including research data management.
Utilization of advanced research computing resources by the UBC research community.
Increased user base for ARC-supported resources; Increased utilization of ARC-supported resources; Increased range of services and resources supported by ARC.
Status: Objective Met
Advanced Research Computing (ARC) continues to support its dedicated computing service to researchers across all disciplines with large data and computational requirements. ARC continues to expand its services and provide training to the research community. The total number of users for Sockeye and Chinook has increased by 31% and 41% respectively compared to last year.
MANAGEMENT AND ADMINISTRATION
Investment in Management and Administration: $9,528,000
Maintain and improve institutional support for research proposal development and grant/award applications.
Grant application success rate; Total annual grant funding.
Maintain indicator performance levels, focus on increasing service levels to internal and external stakeholders; Improved workflow for grant facilitation and pre-award administration.
Status: Objective Met
In 2022/23, UBC received a total of $747,294,149 in research funding from all sources, supporting a total of 9,675 projects. 2022/23 UBC was successful in the Tri-agency grant competitions bolstered by the Support Programs to Advance Research Capacity (SPARC) and Institutional Programs Office (IPO). By working with SPARC, assistant professors in the natural sciences and engineering applying to the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC) have been 1.6 times more likely to be funded. A similar rate of improved success is seen for faculty applying to the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR) Project competition. By working with IPO, researchers successfully attracted infrastructure/equipment awards from the Canada Foundation for Innovation – the average JELF success rate is 80%. In the last CFI’s Innovation Fund competition, UBC’s success rate was 50% compared to the national average of 32%.
REGULATORY REQUIREMENTS AND ACCREDITATION
Investment in Regulatory Requirements and Accreditation: $1,876,452
Implement new opportunities to facilitate meaningful and compliant review of human, animal, and biosafety research protocols.
Improve existing modules in the Research Information Services (RISe) Platform.
Enhance data flows between modules and further develop automations for routine processes.
Status: Objective Met
Research Information System Enterprise (RISe) is the centralized research management system for UBC and our Affiliated Health Institutes. Research Ethics modules are an integral component of RISe, ensuring compliance with, for example, the conflict-of-interest policies, the Tri-Agency Policy Statement on Research with Human Subjects, the Public Health Agency of Canada, and others. To best meet the performance objective, the focus in 2022/23 was placed on ethics and compliance modules. REB Exchange allows RISe to interact with the University of Alberta and the University of Calgary when there is a joint study on human ethics application course research. The teams are gathering requirements, setting up the new workflow, and making a connection to the REB Exchange Server. Work is also underway on the Chemical Safety module, which will provide an online application for researchers.
INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AND KNOWLEDGE MOBILIZATION
Investment in Intellectual Property and Knowledge Mobilization: $380,000
Through enhanced integration of the governance and operations, continue to provide internationally recognized level of service to researchers and external partners through the University-Industry Liaison Office.
Knowledge mobilization metrics such as patenting, licensing, invention disclosures, spin-off company creation, and industry partnerships created.
Maintain indicator performance levels, focus on increasing service levels to internal and external stakeholders.
Status: Objective Met
The UILO continues to work with UBC researchers and industry partners to commercialize research outputs and translate them into impactful treatments, products, and services through mutually beneficial agreements.
Highlights from FY2023 include:
- 1,151 industry-sponsored projects ($68.9M)
- 148 Invention disclosures and 4 new spin-off companies
- 104 Licences or assignment agreements were completed
- UBC researchers filed 219 patents and had 55 patents issued
Improved EDI - Dimensions Pilot Project
Investment in participation in, completion, submission and sharing of Dimensions Action Plan: $500,000
Priority Area: Equity, diversity and faculty renewal (In the content of equity, diversity and inclusion)
- Submission of full application for Dimensions recognition to NSERC, including a finalized Dimensions action plan.
- Response to reviewer feedback and questions as part of multi-stage iterative review process for Dimensions recognition
- Development and communication of outcomes of Dimensions project to broader UBC community through formalized reports, online engagement platforms and university-wide communications
- Monitoring and evaluation of Dimensions-related actions as they are implemented
Completion, submission and recognition of Dimensions Action Plan
Outcomes
- Application for recognition from the federal Dimensions program was submitted in October 2022.
- Following the program's in-depth peer-review process, UBC received a ‘Construction’ designation. This designation reflects that the institution is addressing EDI in a strategic and coordinated way, has implemented and evaluated the impact of past EDI initiatives, and that representational data is being collected and analyzed systematically, but more needs to be done to address obstacles and barriers for equity-deserving groups comprehensively
- UBC’s Action Plan for EDI in Research was developed considering how it can align with, complement, and build upon current work in EDI and anti-racism at UBC while focusing on needs and actions specific to the university’s research ecosystem and community. Implementation of this plan has been integrated within EIO’s StEAR framework.
Status: Complete
Advanced Research Computing (ARC)
Investment in critical digital research infrastructure and support: $4,324,373
Priority Area: Information resources, including digital resources, open access and database
infrastructure for the UBC research community
- Provision of grant application and research data management support by offering consultation on grant applications requiring digital research infrastructure
- Launch of UBC ARC RONIN, part of the ARC Cloud Platform, a user-friendly web application that allows researchers to harness powerful Amazon Web Service cloud infrastructure without learning complex details of cloud computing.
- Launch of Globus, a secure and reliable research data management service for transferring data between a local computer, UBC Sockeye, UBC Chinook, and many research computing endpoints worldwide.
Enhanced critical digital research infrastructure available to support the UBC research community
Outcomes:
- ARC held several workshops with the research community to consult and develop the research data management plan strategy.
- ARC successfully launched two new cloud computing and data transfer services, UBC ARC RONIN and Globus Plus. These systems have user-friendly web interfaces, allowing users to use the services without learning the complex details of cloud computing. ARC will launch new programs enabling the researchers to participate and partner with ARC to evaluate new, nascent, and emerging technologies that help deliver high-impact required services and tools. Globus Plus expands the data management platform that allows users to securely and reliably transfer data between a local computer and research computing endpoints. The number of users increased for both UBC Sockeye and UBC Chinook.
Status: In Progress
Plant Care SErvices
Investment in facility renewal process and infrastructure: $378,000
Priority Area: Facilities renewal, including deferred maintenance
dedicated to enabling researchers’ projects and supporting teaching and training
- Holding consultations, providing advice and technical support for experimental design and set up with researchers.
- Providing hydroponic nutrition, integrated pest control and climate control in accordance with individual needs of researchers.
- Hosting orientation sessions on the proper use of equipment and safety practices for trainees.
- Maintaining and improving infrastructure to ensure excellent facilities for the research community.
Improved services and facilities provided to the UBC community by Plant Care Services
Outcomes: Improved services and facilities provided to the UBC community by Plant Care Services. Plant Care Services is a shared research platform for greenhouse and field scientific experiments. In FY23, 154 different projects took place at the three facilities under the Plant Care Services. It provided climate control, integrated pest management, and hydroponic nutrition to meet researchers' individual needs. PCS works closely with companies on industry development and consultation. PCS is working closely with private companies to facilitate industry knowledge.
Status: In Progress
Global Research Excellence Institutes – BioProducts Institute
Investment in partnership and funding development, and commercialization activities: $885,000
Priority Area: Innovation and commercialization activities
- Establishing impactful global partnerships
- Accelerating research grant funding
- Increasing commercialization outputs
New partnerships, funding and/or commercialization and knowledge mobilization activities
Outcomes: Since its inception, the Bioproducts Institute has developed partnerships with BC Pulp and Paper BioAlliance and various government agencies, including NSERC, Pacifican, NRCan, Mitacs, and BC Government. Notable new partnerships for this reporting period include collaborations with international industry partners and BC Ministry of Forests. BPI researchers have established UBC as Canada’s bio-based materials and bioproducts research epicenter. The grants awarded in the area of ‘cellulose, lignin & cellulases’ indicates that UBC’s funding was the highest in Canada and over three-fold higher than that of the next counterpart, with UBC’s research funding in the area increasing by 200% since 2012. BPI research translates into start-ups. Five ventures are being incubated. Two notable developments with impact took place in the form of Sustainable apparel and footwear and Bioproducts to address the plastic pollution crisis (Biofoam).
Status: In Progress
Expansion of Research Security Activities
Investment in staffing and training: $400,000
IPG Priority Area: Research Security
- Hiring staff focused on performing risk assessments and due diligence
- Creation of informative materials for scholars and researchers
- Staff training
Increased support for risk assessments and enhanced support for researchers and scholars
Outcomes:
- To bolster support for risk assessments and aid researchers and scholars in the field of Research Security, UBC recruited research security staff at both campuses.
- Additionally, current staff at UBC's University-Industry Liaison Office further supported the faculty.
- Furthermore, we conducted numerous training sessions for faculty and staff to keep them abreast of the latest developments in the research security domain.
Status: In progress
Enhanced IT Measures
Investment in cybersecurity infrastructure and measures: $1,968,707
IPG Priority Area: Research Security
Indicators:
- Subscribe to online database for identifying sanctions, security threats, and export controls
- Continued investment to increase capacity to protect researchers and their data from the risk of cyberattacks and breaches.
- Continued rollout of protection and response systems for servers and workstations used by researchers and multi-factor authentication.
Target Outcomes:
Enhanced cybersecurity environment for researchers
Outcomes:
- UBC has subscribed to various IT companies to enhance the IT security measures further for identifying sanctions, security threats, and export controls and protecting data from the risk of cyberattacks and breaches.
- We continue to roll out protection and response systems for servers and workstations used by the UBC research community.
- We continue to foster a culture of security awareness and responsibility among researchers and staff for adherence to the security protocols.
Status: In progress
FACILITIES
Further develop and maintain new and existing research facilities.
Amount of significantly renovated research space.
Increase efficiency, capacity and effectiveness of space utilization through reconfiguration of facilities and research spaces.
Status: Objective Met
UBC’s planned renovations of research spaces are proceeding as scheduled. UBC’s Pulp and Paper Centre lab spaces were renewed and upgraded, the Macleod Building’s envelope, mechanical and electrical systems were replaced, and a number of new constructions on campuses are proceeding as planned.
RESOURCES
Expand UBC's advanced research computing (ARC) support by enabling greater access to and utilization of UBC ARC Chinook and other advanced research computing resources, including research data management.
Utilization of UBC ARC Chinook and other advanced research computing resources by the UBC research community.
Increased user base for ARC-supported resources; Increased utilization of ARC-supported resources; Increased range of services and resources supported by ARC.
Status: Objective Met
Advanced Research Computing is UBC’s dedicated service for researchers across all disciplines working on questions that have large data and computational needs. ARC is continuing to expand its services and has launched ARC RONIN and Globus Plus cloud computing and data transfer services. The ARC Chinook, an object storage platform with an initial 5 PB of storage, allows users to retain and retrieve portions of large research datasets composed of files and unstructured data
MANAGEMENT AND ADMINISTRATION
Maintain and improve institutional support for research proposal development and grant/award applications.
Grant application success rate; Total annual grant funding.
Maintain indicator performance levels, focus on increasing service levels to internal and external stakeholders; Improved workflow for grant facilitation and pre-award administration.
Status: Objective Met
In 2021/22, UBC received a total of $773,686,504.82 in research funding from all sources, supporting a total of 10,218 projects. 2021/22 UBC was successful in the tri-agency grant competitions, with above national average success in the SSHRC Insight Grant and NSERC Discovery grant.
REGULATORY REQUIREMENTS AND ACCREDITATION
Implement new opportunities to facilitate meaningful and compliant review of human, animal, and biosafety research protocols.
Improve existing modules in the Research Information Services (RISe) Platform.
Complete transition to the online Research Project Information Form (RPIF) and enhance data flow between modules.
Status: Objective Met
Research Information System Enterprise (RISe) is the centralized research management system for UBC and our Affiliated Health Institutes. Research Ethics Board (REB) module is an integral component of RISe ensuring compliance with, for example, the conflict of interest polices, the Tri-Agency Policy Statement on Research with Human Subjects, the Public Health Agency of Canada, and others. To best meet the performance objective, focus in 2021/22 was placed on the Research Ethics Board (REB) Module. UBC and Research Ethics BC (REBC) are leading ethics harmonization efforts to streamline ethics review and approval process, allowing for submission of a single ethics application across partner institutions. Two new members have joined the harmonization process in the past year.
INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AND KNOWLEDGE MOBILIZATION
Through enhanced integration of the governance and operations, continue to provide internationally recognized level of service to researchers and external partners through the University-Industry Liaison Office.
Knowledge mobilization metrics such as patenting, licensing, invention disclosures, spin-off company creation, and industry partnerships created.
Maintain indicator performance levels, focus on increasing service levels to internal and external stakeholders.
Status: Objective Met
The UILO continues to work with UBC researchers and industry partners to commercialize research outputs and translate them into impactful treatments, products and services through mutually beneficial agreements.
Highlights from FY2022 include:
- 1,436 industry sponsored projects ($80.3m)
- 161 Invention disclosures and 10 new spin-off companies
- 115 Licences or assignment agreements were completed
- UBC researchers filed 353 patents, and had 99 patents issued
Improved EDI - Dimensions Pilot Project
Objectives
- Continued assessment of informational gaps and identified barriers and obstacles experienced by equity-deserving groups to inform the self-assessment efforts
- Drafting of the action plan complement and built upon existing UBC strategies, such as the Inclusion Action Plan and Indigenous Strategic Plan
- Submission of the application to the Tri-Agencies for recognition of UBC as a Dimensions institution
Outcomes
- The UBC Dimensions institutional self-assessment is complete, including a complete list of EDI-related UBC policies, programs, practices and initiatives, and direct feedback from equity-deserving groups that identify gaps and barriers in the university’s EDI efforts.
- The UBC Dimensions action plan is complete and has been endorsed by university leadership, including the President. The action plan involved consultation and feedback from a many senior leadership and administrative offices and units across both campuses to ensure actions were feasible and confirm the persons responsible for their implementation and monitoring.
- UBC’s full Dimensions application is nearly complete. A letter of endorsement from President Ono, a requirement for the application, has been obtained as part of the application package. The full application package will be submitted in the fall of 2022
Status
- Achieved
- Achieved
- In Progress
Integrated Renewal Program - Workday RISe systems integration
Objectives
Continue to refine the integration, ensuring that the biannual Workday updates work with RISe, and focus on providing comprehensive reporting mechanisms and data flow to stakeholders
Outcomes
RISe-Workday integration continues to play an important role in the efficient operations of research administration. With the enhanced system security protocols, more granular data, a robust financial account administration and reporting, RISe and Workdays teams were successful in optimizing data transactions between systems allowing for a faster turnaround on processes. The RISe team reviewed and streamlined the existing user-run reports to provide access to the information pertinent to users’ requests, consolidate fragmented reports to enhanced queries with user-specified search parameters, and built new reporting capacities for additional internal and external statistical reporting.
Status: Achieved
Advanced Research Computing
Objectives
Improve access to digital research infrastructure by increasing storage, compute, network, and data centre capacity for UBC researchers
Outcomes
ARC was successful in launching two new cloud computing and data transfer services, UBC ARC RONIN and Globus Plus. These systems have user-friendly web interface allowing users to use the services without having to learn complex details of cloud computing. Globus Plus expands the existing capacity of the research-focused data management platform that allows users to securely and reliably transfer data between a local computer and research computing endpoints. ARC held a number of tailored workshops with the research community to consult and develop the research data management plan strategy. ARC held a series of workshops and bootcamps to promote its services and educate the community about advanced research computing.
Status: In Progress
Plant Care Services
Objectives
Continue offering the services by a team dedicated to enabling researchers’ projects and supporting teaching and training
Outcomes
Plant Care Services is a shared research platform for greenhouse and field scientific experiments. PCS is a full-service facility and its personnel provide advice and support for experimental design, execution of field experiments, and training to graduate students and other trainees. In FY22, there were 171 different projects that took place at the three facilities under the Plant Care Services
Status: In Progress
Global Research Excellence Institutes – BioProducts Institute
Objectives
Developing key partnerships with internal and external stakeholders
Outcomes
The BioProducts Institute (BPI) is an innovative ecosystem of high-impact fundamental and applied researchers working on research themes centered around biocatalytic transformation and engineering of biomass, bio-nanoparticle enabled materials, bio-based polymers and carbon materials, and biorefinery and biofuels systems. In the FY22, BPI was successful in partnering with a number of major industry and academic partners to further promote innovations and collaborations in biobased solutions. BPI joined the International Academy of Wood Science, signed a statement of cooperation with the Natural Resources Institute Finland (Luke), and signed a statement of cooperation the Swiss Federal Laboratories for Materials Science and Technology (Empa).
Status: In Progress
FACILITIES
Support existing shared research platforms and ensure their ongoing operation during and following the impact of COVID-19. Establish the Facility for Infectious Disease and Epidemic Research (FINDER) as a new shared research platform at UBC.
Launch of FINDER under new governance and staffing structure to operate as a shared research platform.
Maintain existing shared research platforms that provide essential services for researchers. Establishment of FINDER as a new shared research resource at UBC.
Status: Objective Met
The Facility for Infectious Disease and Epidemic Research (FINDER) is now a shared research platform at UBC for Containment Level 3 (CL-3) scientific experiments. The platform is operated by a team of expert staff supported by the VP Research & Innovation Office and a scientific advisor. Governance of the platform is via a Steering Committee comprising users and administrators. In its first year of operation, it has catered to the needs of 22 researchers and 11 Principal Investigators from various departments within the Faculties of Science and Medicine. The facility provides: space for working with Risk Group 3 pathogens, such as SARS-CoV-2; expert research planning advice; certification for working in CL-3 environments and technician support.
RESOURCES
Expand UBC's advanced research computing (ARC) support by enabling greater access to and utilization of UBC ARC Sockeye and other advanced research computing resources, including research data management.
Utilization of UBC ARC Sockeye and other advanced research computing resources by the UBC research community.
Increased user base for ARC-supported resources; Increased utlization of ARC-supported resources; Increased range of services and resources supported by ARC.
Status: Objective Met
UBC ARC continues to improve advanced research computing resources for the research community. Among the many resources available, Sockeye is a high-performance computing platform available to UBC researchers across all disciplines. With nearly 16,000 CPU cores and 200 GPUs, Sockeye is designed to significantly increase UBC’s computing capacity and supplements the national platform for digital research infrastructure in order to meet the immediate needs of UBC researchers. As a result of the pandemic training was transitioned from in person to online, where it has resulted in greater participation. ARC has increased its Sockeye user base, which includes faculty members, staff and students from 351 to 659 while also increasing the range of services available to the research community such as: storage, data capture platforms, access to high performance computing.
MANAGEMENT AND ADMINISTRATION
Maintain and improve institutional support for research proposal development and grant/award applications.
Grant application success rate; Total annual grant funding.
Maintain indicator performance levels, focus on increasing service levels to internal and external stakeholders; Improved workflow for grant facilitation and pre-award administration.
Status: Objective Met
UBC’s Support Programs to Advance Research Capacity (SPARC) unit is focused on supporting research proposal development across the institution, though various services including: information sessions, one-on-one consultations, and internal review panels. In light of the pandemic SPARC is providing all info sessions online while also recording the sessions for later viewing to allow for greater access. SPARC moved away from PDF resources (strategic guides) to web-based resources that are more easily updated with last minute sponsor advice and can be viewed on multiple platforms.
In 2020/21, UBC received a total of $759,097,528.51 in research funding from all sources, supporting a total of 10,116 projects. Overall totals were significantly impacted by government and Tri-Agency funding in response to the COVID-19 pandemic. Pandemic notwithstanding, in 2020/21 UBC was successful in the tri-agency grant competitions, with above national average success in the SSHRC Insight Grant and NSERC Discovery grant.
The need for administrative staff to work remotely this reporting period created an opportunity to consider new efficiencies in pre-award workflow. The Office of Research Services (ORS) moved its operations fully online in FY21 including streamlining grant review processes, expanding web content on the ORS website on grant application procedures, and exclusively using online/electronic forms to reduce administrative paperwork.
REGULATORY REQUIREMENTS AND ACCREDITATION
Implement new opportunities to facilitate meaningful and compliant review of human, animal, and biosafety research protocols
Improve existing modules in the Research Information Services (RISe) Platform
Complete the Conslidated Laboratory database Biosafety compliance integration; Update REB Clinical Forms; Update Conflict of Interest module
Status: Objective Met
Research Information System Enterprise (RISe) is the centralized research management system for UBC and our Affiliated Health Institutes. Managing over $650m annually it is essential to ensure continued compliance with rules established by, for example, the Tri-Council Policy Statement on Research with Human Subjects, the Public Health Agency of Canada, the Canadian Food Inspection Agency, and with financial conflict of interest rules in the United States.
INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AND KNOWLEDGE MOBILIZATION
Through enhanced integration of the governance and operations, continue to provide internationally recognized level of service to researchers and external partners through the University-Industry Liaison Office.
Knowledge mobilization metrics such as patenting, licensing, invention disclosures, spin-off company creation, and industry partnerships created.
Maintain indicator performance levels, focus on increasing service levels to internal and external stakeholders.
Status: Objective Met
The UILO continues to work with UBC researchers and industry partners to commercialize research outputs and translate them into impactful treatments, products and services through mutually beneficial agreements. Highlights from FY2021 include:
- UBC was the number one Canadian university listed in a 2020 report on the Top 100 Worldwide Universities Granted U.S. Utility Patents; filed 254 patents, and had 94 patents issued.
- UBC ranks first in the world in innovation and industry partnerships in latest Times Higher Education Impact Rankings; UBC had 1,353 industry sponsored projects ($62.2M).
- 253 Licences or assignment agreements were completed.
- 164 Invention disclosures and 14 new spin-off companies
Incremental Project Grant
Project Objective
entrepreneurship @UBC (e @UBC) is the University’s incubator and accelerator program for new ventures that arise from innovative, translational research at UBC. Their mission is to “help UBC entrepreneurials change the world”. e @UBC enables entrepreneurial faculty, students and alumni to take ideas out of the lab or classroom , and explore and develop their commercial potential. Targeted, proven programs such as the Lean Launch Pad (LLP), expert mentors, and UBC’s success as a research-intensive university provide a rich ecosystem to enable e @UBC ventures. With streams in clean tech, the life sciences, and social entrepreneurship, e @UBC enables concrete economic and social impact locally, provincially, and beyond. The e @UBC program is a key way in which the university supports new entrepreneurs to get their start and helps to build new ventures coming out of research and the business ideas of our students, faculty, staff and alumni..
e @UBC’s objectives for 2020/21 are to continue to expand the number and diversity of new ventures participating in its incubator program streams, to increase the number of students supported by the Lean Launch Pad Program, and to increase the number of Entrepreneurs-in-Residence. The funding received from the Incremental Project Grant program will contribute directly to meeting those objectives.
In meeting this objective, e @UBC will demonstrate:
• Increase in number of ventures applying to and supported by e @UBC’s thematic incubator programs, Lab2Launch, Core Technology, and Social Impact
• Increase in number of students participating in e @UBC’s entrepreneurial development programming (which include internships, workshops, speaker series and for-credit courses)
• Increase in number of ventures exiting the e @UBC accelerator platform, and a corresponding increase in the amount of venture capital these emerging companies attract.
# New Ventures
# Students participating
- e @UBC had its highest venture enrollment to date, marking a 6% increase from the previous year.
- This year provided internships for 120 students and trainees; engaged with 586 UBC students through various events, such as entrepreneurship @UBC Immersion Week, and Community Town Halls and Speaker Series
- Launched a Community Town Hall series to help keep the community connected with updates, venture asks and exposure to key learnings from e @UBC ventures, mentors and alumni.
Project Objective
More and more, public institutions are expected to have a meaningful impact that benefits the broad society. Innovation UBC is our framework to take research and scholarship beyond the University to enable meaningful social and economic impact. Commercialization, entrepreneurship, knowledge exchange and partnership development are the four pathways by which Innovation UBC will deliver this impact.
Following last year’s objective to establish and embed Innovation UBC as the central hub for innovation activity at UBC, this year’s objective will be to implement a coordinated and strategic operation plan to create research partnerships, commercialize research and exchange knowledge at UBC.
In meeting these objectives, Innovation UBC will enable:
• Emergence of new research partnerships
• New knowledge exchange opportunities with community groups and government
• New opportunities to commercialize and transfer breakthrough research discoveries to innovative partners
- # new research partnerships
- # new knowledge exchange opportunities
Innovation Partnerships:
- Implemented new programming and research around COVID to support major corporate partner
- Enabled the re-invigoration of the Campus As A Living Lab mechanism for connecting the campus, researchers and research partners to address climate and sustainability questions
- Implemented new programming around taking research to innovation and impact
- Continued and amplified new programming to orient UBC faculty and students to forming industry partnerships
- Formed new relationships with 12 new corporate partners around potential research collaborations
- UBC involved in another 14 Technology Leadership projects in collaboration with Canada's Digital Technology Supercluster.
Knowledge Exchange
- Engaged over 500 participants in 17 events and workshops
- Created a Kx training program
- Created an online capsule for graduate students
Project Objective
Research Information System Enterprise (RISE) is the centralized research management system for UBC and our Affiliated Health Institutes. Managing over $650m annually in research funding as well as all human ethics, animal care, biosafety, radiation safety, conflict of interest, and BC provincial research ethics platform requirements. RISE provides an essential streamlined business workflow to the UBC research community.
In 2020/21, RISE will continue to expand the reporting capabilities of RISE by developing a data lake concept and reporting tools. This will both simplify and provide better self-service for the research community. Additionally, RISE reporting tools will be redeveloped to meet changing institutional needs.
In meeting these objectives, RISE will demonstrate:
• Increase in data elements available for reporting
• Increase in numbers of reports available
• Enhanced reports and uptake from the research community
Qualitatively, these improvements will not only provide more accurate reporting, but can also be used to drill institutional-level information on such things such as networks of interdisciplinary researchers focused on solving key challenges facing society that transcend the traditional boundaries associated with departments, institutions, and funding agencies
- # Data elements
- # Reports
- RISe total data elements available for reporting increased from 52 to 102.
- Number of total reports decreased by an estimated 20% due to data consolidation and mergers.
- We have developed a Data Lake, further enhancing ad hoc reports. We are now able to run analytics on live research funding data faster, without having to move the data to separate systems, ultimately improving decision making.
Project Objective
UBC is one of 17 institutions included in the Dimensions: equity, diversity and inclusion Canada pilot program (Dimensions). UBC is committed to fostering increased research excellence, innovation and creativity across all disciplines through increased equity, diversity and inclusion. Dimensions is intended to identify and address obstacles and barriers faced by, but not limited to, women, Indigenous Peoples, persons with disabilities, members of visible minority/racialized groups, and members of LGBTQ2+ communities within the research ecosystem.
Inclusion is a major focus and one of three key themes of UBC's strategic plan, Shaping UBC’S Next Century, which recognizes that sustained excellence in research, education and engagement depends on the integration of diverse perspectives and approaches. A system-wide approach to diversity, equity and inclusion, Inclusive Excellence, is a key commitment of the plan and several initiatives to support this commitment are already underway. This includes the university developing its first Inclusion Action Plan, the establishment of several senior advisory positions that guide university leadership on dimensions of equity and inclusion, and the completion and implementation of a renewed Indigenous strategic plan which will further UBC’s commitment to enact meaningful and lasting reconciliation.
This year, the project aims to do the following:
- Complete its comprehensive institutional self-assessment of EDI-related policies, program, practices and initiatives in order to identify barriers experienced by equity-deserving groups.
Address these barriers through the development and implementation of a Dimensions action plan as a way to progress positive change within the UBC research ecosystem.
- Development of an action plan to create and sustain an equitable and inclusive campus environment.
- Submission of a full application to the Tri-Agencies to obtain institutional Dimensions recognition
- Completed the establishment of a Self-Assessment Team to coordinate a comprehensive environmental scan of EDI programs, policies, and initiatives in order to identify barriers or obstacles experienced by equity-deserving groups.
- Completed the creation of a Self-assessment Approach, which outlines the scope and breadth of the UBC Dimensions project, as well as identifies the assessment questions that will be answered by the self-assessment and environmental scan.
- Completed the quantitative portion of the institutional self-assessment on EDI in research.
Project Objective
The Integrated Renewal Program is a multi-year large scale initiative aimed at renewing and updating existing UBC administrative processes and systems to better support the changing needs of our dynamic community and Institution. By modernizing and simplifying processes and bringing them into an intuitive integrated system – Workday - we will enable the UBC community to spend more time on strategic priorities. Key objectives of this initiative are to support an engaged, collaborative, and exceptional learning, research, and working environment for students, staff, and faculty, and to ensure reliable, integrated, and accessible institutional data that enables people to make informed, strategic decisions.
Support from the Incremental Project Grants will be critical in ensuring a seamless integration of the new Workday system and UBC’s centralized research management system (RISe). The objectives for 20/21 are to effectively integrate the two systems to enable continuous data communication and to successfully launch the renewed system to enhance the grant administrative support while minimizing the impact to the UBC research community.
In meeting these objectives, we will:
• Increase the number of linkages between RISe and Workday
• Streamline data sharing and communication between RISe and UBC systems
• Create a simple, intuitive, and consistent user experience
- # linkages between RISe and Workday
- To date we have increased the number of linkages between RISe and Workday from 4 to 6, and anticipate further increases next year.
- We continue to streamline data sharing and communication between the two systems by creating automations, where 50% of activities are pre-filled or transferred information thus reducing the need for user input and reducing errors due to manual inputs
FACILITIES
Develop and further establish the new Plant Care Services shared facility.
Operational and governance plans Plant Care Services are implemented
- Increased number of new and returning users from baseline
- Profile of users reflects the multi-disciplinary nature of researchers in this space
Status: Objective Met
Plant Care Services is now an established shared research platform at UBC. The platform is operated by a team of expert staff supported by the VP Research & Innovation Office and a scientific advisor. Governance of the platform is via a Steering Committee comprising users and administrators. In its first year of operation, Plant Care Services catered to the needs of 26 researchers, 30% of which were new to greenhouse or field research at UBC. These researchers directed 157 projects with the help of 88 trainees. Users hail from various departments in the Faculties of Science, Forestry, Land and Food Systems, Applied Sciences and Arts, and the horticulture sector in British Columbia. Plant Care Services also hosted two undergraduate courses. Plant Care Services, a crucial service at UBC, maintained its operations during the research curtailment period due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
RESOURCES
Improve the functionality and access to the Researcher Information Service (RISe) platform with new modules
Number of new RISe modules
- Retrofit RISe with new functionality and develop and implement integration pathway with the new financial system scheduled to be deployed in FY21
- Integration of existing financial data into the new finance system to enable ongoing management of research funding
Status: Objective Met
UBC is transitioning its human resources- and financial management systems to a new cloud-based platform called WorkDay. The Research Information Services (RISe) system will remain UBC’s platform for grant management, REB and other reviews and approvals, and seamless integration in the transition to WorkDay is essential for our researchers and scholars. A team of research finance personnel are leading the technical integration of these two platforms, which will be complete when the new system goes live later this year. Ongoing training for the research community to help manage this integration is ongoing.
MANAGEMENT AND ADMINISTRATION
Establish refreshed model for management of major prizes and awards
Refreshed Prizes & Awards function is implemented
- Implement new Prizes & Awards strategy
- Diversity of nominations for major prizes and awards
Status: Objective Met
A new strategy was implemented over the last year to further support the success and recognition of UBC scholars and researchers in major national and international prizes and awards, and to focus on equity, diversity and inclusion in award nominations. The new strategy provides greater support for the development of awards pathways for early-career researchers, increasing discipline-specific support and identifying progressive series of relevant prizes and awards at different career stages. The role of a reconfigured advisory committee includes helping to establish these pathways, while providing advice to the VP Research & Innovation on strategic priorities and planning for major award programs.
REGULATORY REQUIREMENTS AND ACCREDITATION
Implement new opportunities to enable meaningful and compliant review of human, animal, and biosafety research protocols
Improve existing modules in the Research Information Services (RISe) Platform
- Retrofit RISe data structure with the new finance system to ensure seamless compliance between human, animal and biosafety research protocols with funded research projects
Status: Target Met
Integration of the Research Information Services (RISe) with the University’s new finance and human resources management systems is essential to ensure continued compliance with rules established by, for example, the Tri-Council Policy Statement on Research with Human Subjects, the Canadian Council on Animal Care, and with financial conflict of interest rules in the United States. The data structure in RISe will be successfully integrated into the new system, WorkDay, when it goes live and will allow faculty and staff to maintain regulatory compliance without any interruption to their programs of research.
INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AND KNOWLEDGE MOBILIZATION
Establish the Innovation Partnerships function as a core element of the Innovation UBC strategy
Innovation Partnerships function is established and recognized at the University
- Research partnerships
- Diversity of research partners
- Partnerships involving Canada’s Digital Technology Supercluster
Status: Target Met
Innovation UBC is the University’s framework to help deliver on a commitment to generating knowledge that creates a lasting impact on society. The Innovation Partnerships function is established now as a hub to connect external partners from industry, government and the not-for-profit sectors with UBC scholars and researchers who can collaborate on problems that face society and business. New and expanded partnerships have been created in the technology, life-sciences, and natural resources sectors.
Incremental Project Grant
Project Objective
entrepreneurship @UBC (e @UBC) is the University’s incubator and accelerator program for new ventures that arise from innovative, translational research at UBC. Their mission is to “help UBC entrepreneurials change the world”. e @UBC enables entrepreneurial faculty, students and alumni to take ideas out of the lab, and explore and develop their commercial potential. Targeted, proven programs such as the Lean Launch Pad, expert mentors, and UBC’s success as a research-intensive university provide a rich ecosystem to enable e @UBC ventures. With streams in clean tech, the life sciences, and a growing number of social ventures, e @UBC enables concrete economic and social impact locally, provincially, and beyond.
e @UBC’s objectives for 2019/20 are to expand the number and diversity of new ventures participating in its program streams, to increase the number of students supported by the Lean Launch Pad (LLP) Program, and to increase the number of Entrepreneurs-in-Residence. The funding received from the Incremental Project Grant program will contribute directly to meeting those objectives.
In meeting this objective, e @UBC will demonstrate:
- Increase in number of ventures applying to and supported by e @UBC’s incubator platform;
- Increase in number of students participating in e @UBC’s entrepreneurial development programming (which include internships, workshops, speaker series and for-credit courses)
- Increase in number of ventures exiting the e @UBC accelerator platform, and a corresponding increase in the amount of venture capital these emerging companies attract.
These are the key performance indicators for e @UBC programming. Important outcomes are the health, economic, and social benefits that successful ventures bring to the world. Acuva, an e @UBC success story, empowers customers globally to produce safe drinking water. HeadCheck Health was formed in 2012, and provides an app that runs today’s most well-researched and highly-regarded concussion tests, enabling real-time documentation, assessment and reporting of concussion injuries. Brighter Investment is a social venture that provides investors with the opportunity to back the engineers, doctors and scientists of the future in the developing world.
UBC’s entrepreneurs can change the world. The e @UBC program is a priority for the University, and is where we want our entrepreneurs to get their start.
# New Ventures
# Students participating
- six-fold increase year over year in # of students engaged in e @UBC programs;
- 100+ ventures accepted into e @UBC programs;
- 58 student founders whose work is supported by 14 entrepreneurs-in-residence.
Project Objective
More and more, public institutions are expected to have a meaningful impact that benefits the broad society. Innovation UBC is our framework to take research and scholarship beyond the University to enable meaningful social and economic impact. Commercialization, entrepreneurship, knowledge exchange and partnership development are the four pathways by which Innovation UBC will deliver this impact.
Innovation UBC expands on the established support at UBC, providing new services and reconfiguring existing services to offer a simplified and more efficient means of engagement for researchers and external partners. A primary objective for this year is to raise awareness of how this innovation ecosystem is organized and how services are accessed. A second objective will be to implement coordinated strategic and operational plans that embed Innovation UBC as the central hub for innovation activity at the University. The ultimate success of Innovation UBC will be evidenced by the emergence of new research partnerships, new knowledge exchange opportunities with community groups and government, and new commercial opportunities. Outcomes of these activities could range from new policy directions for government, new therapies for disease, and new technologies that benefit society.
As a building year for Innovation UBC, building presence and visibility, more immediate measurements of the success will include:
- the number and diversity of researchers and partners looking to access services and understand the innovation ecosystem at UBC.
- hosting and participating in a wide variety of events and activities that will provide an opportunity for our researchers and scholars to engage directly with people who can benefit from our work.
- These will include collision opportunities for researchers and industry, public lectures and performances that enable innovative forms of knowledge exchange, and competitions amongst our entrepreneurs who will be the employers of tomorrow. Attendance – both in number and in diversity of audiences – will be key indicators of the success of these forms of engagement.
This is a building year for Innovation UBC that will allow us to test and refine the model, and the ways by which we deliver innovation with impact. The Institutional Project Grant will directly benefit our innovation ecosystem, through support for the range of activities and initiatives we plan to undertake.
Innovation Partnerships
- New partnership funding
- New programs
Knowledge Exchange
- Kx metrics
Innovation Partnerships:
- Implemented new programming to support major corporate partner
- Implemented new programming to orient UBC facutly and students to forming industry partnerships
- Formed new relationships with 6 new corporate partners around potential research collaborations
- UBC involved in 12 Technology Leadership and 2 Capacity Building projects in collaboration with Canada's Digital Technology Supercluster.
Knowledge Exchange
- In its first full year, the Kx unit engaged over 400 participants in 12 events and workshops, published a Kx toolkit for graduate students, and participated in five pan-Canadian collaborative projects.
Project Objective
Research Information System Enterprise (RISE) is the centralized research management system for UBC and our Affiliated Health Institutes. Managing over $650m annually in research funding as well as all human, animal, biosafety and conflict of interest requirements, RISE provides streamlined business workflow to the community.
RISE’s objectives for 2019/20 are expand the reporting capabilities of RISE by introducing new data sources available through integration with the new financial system, expand reporting on existing data, and provide better and more meaningful reports from the data.
In meeting this objective, RISE will demonstrate:
- Increase in data elements available for reporting
- Increase in numbers of reports available
- Enhanced reports for the research community
These are the key performance indicators for RISE. Important outcomes are better, and more accurate, reporting. For example, data can be used to identify and provide information on such things as research clusters which are interdisciplinary networks of researchers focused on solving key challenges facing society that transcend the traditional boundaries associated with departments, institutions, and funding agencies. UBC is committed to supporting the development of clusters of research excellence.
- Data elements available for reporting
- # Reports
- Report quality
- RISe total data elements increased from 38 to 107 on financial related data elements with WorkDay integration
- Number of total report available was reduced as several were merged to simplify the system for ease of use. Two data lakes are currently under development to further enhance ad hoc reports by business owners to enable tailor made solutions for their reporting requirements.
- With RISe being the master system of record on most fields for research, 100% alignment on research reporting quality has been realized between the RISe and Workday systems
FACILITIES
Further develop shared infrastructure
Number and maturity of shared infrastructure initiatives.
- Governance models for new initiatives are in place;
- Fully costed funding models for new initiatives are in place;
- Planning and priority-setting for future initiatives is in place.
Status: Objective Met
UBC launched the new Plant Care Services shared facility in early 2019. This platform has engagement and support from three faculties, a sustainable budget model, and an effective governance structure. Plans are ongoing to prioritize additional shared facilities.
RESOURCES
Improve the functionality and access to the Researcher Information Service (RISe) platform with new modules..
Number of new RISe modules
- Online grant submission module complete;
- Prioritized work plan in place and approved for new and refreshed modules.
Status: Objective Met
Grant submission business analysis was completed which will assist the research community in timely and more accurate grant proposals. As part of this, a new module went through discovery and architecture sessions for management of the Centres and Institutes that can span multiple academic units. Also UBC launched the Indirect Cost of Research Rates (ICR) information module in 2019 . This enabled UBC RISe users which include researchers and research administrators to look up Sponsor and related programs for the applicable ICR rate in RISe to enable accurate budgeting.
MANAGEMENT AND ADMINISTRATION
Improve workflow efficiencies in pre-award administration.
Processing time and accuracy of pre-award documentation.
- Improved accuracy in pre-award documentation;
- Improved workflow between Research Finance and grants administration;
- Improved workflow for sponsored research contracts and Research Finance.
Status: Objective Met
Pre-award business and technical function groups improved SOP documentation which has improved the pre-award process for the community enabling more timely support. Workflow was improved to assist in the integration of more, and more accurate financial data between RISe and PeopleSoft. As part of this, a focus on contract research workflow improvements, enabled more accurate indirect cost allocations reducing the administrative overhead from previous years.
REGULATORY REQUIREMENTS AND ACCREDITATION
Implement new opportunities to enable meaningful and compliant review of human and animal research protocols
New modules in the Research Information Services platform.
- Implementation of module to facilitate the BC Ethics Harmonization Initiative, a provincial resource to facilitate transformational health system research that crosses institutional and geographic boundaries;
- Development of a Pedagogical Merit Review module for animal care teaching protocols, in response to a CCAC finding on a recent site review.
Status: Objective Met
The Provincial Research Ethics Platform (PREP) that enables provincial research ethics harmonization was implemented in 2018, and has had a meaningful impact on the efficiency of the ethical review of studies being conducted at multiple BC institutions. The Pedagogical Merit Review module is operational, and satisfies the CCAC recommendation.
INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AND KNOWLEDGE MOBILIZATION
Develop robust knowledge mobilization plan, as one of four pathways for Innovation UBC.
New Knowledge Exchange unit is established and recognized at the University.
- Knowledge Exchange unit established;
- Associate Director, Kx is in-post
- Draft strategic and operational plans are prepared following broad stakeholder consultation.
Status: Objective Met
The Associate Director, Knowledge Exchange was successfully recruited to UBC in 2018. Operational and strategic plans are in development, and an advisory committee representing a broad group of stakeholders is in place. The Unit is becoming recognized as a go-to resource for knowledge exchange expertise.
Incremental Project Grant
Project Objective
Develop and maintain entrepreneurship @UBC (e @UBC) a unique program that delivers a combination of education and venture creation, to maximize the number of successful ventures coming out of UBC. Timelines Apr 2018 – Mar 2019, Project to be ongoing in future years.
- Program participation
- # EIRs
- # New Ventures
- The number of ventures moving through the Lean Launch Pad program has increased year-over-year, creating more opportunities for UBC students, faculty and alum.
- Implemented second program area - entrepreneurial development
- New program area and increase in new ventures has resulted in additional Entrepreneurs in Residence and a broader range of expertise available to program participants.
Project Objective
The Innovation UBC network helps transform research and entrepreneurial drive into new products, policies and practices that improve lives around the world. Funding to be used for hiring employees and renovating facilities and improving visibility for Innovation UBC offices and hubs. Timelines Jan – Mar 2019
- Online presence
- Staff recruitment to this new team
- www.innovation.ubc.ca launched in April, 2018
- Director, Corporate Relations in-post
- Two Innovation Development Officers in-post
Project Objective
Development and maintenance of the Research Information Services Enterprise (RISE) system for enhanced compliance, data access and reporting. Timelines Apr 2018‐ Mar 2019. Project to be ongoing in future years
- # New Modules
- planned
- implemented
New modules proceeded on schedule to help improve the efficiency of researchers applying to a harmonized research ethics process in BC, and to our Animal Care Committee.
FACILITIES
Increase the research capacity of UBC by renovating and/or and maintaining new and existing research facilities
Amount of significantly renovated research space
Increase efficiency, capacity and effectiveness of space utilization through reconfiguration of facilities such as the Sequencing & Bioinformatics Consortium and the Biomedical Research Centre
Status: Objective Met
New capacity was created for the Sequencing & Bioinformatics Consortium, and a range of new facilities were created in the Biomedical Research Centre. Reconfiguration of certain animal care facilities was also undertaken in anticipation of new accreditation that is anticipated in 2019.
RESOURCES
Increase access to research resources and performance data such as the Sequencing & Bioinformatics Consortium, and by maintaining and expanding library resources and online tools such as UBC’s Open Collections project, and the Health Data Asset Inventory.
Volume of library holdings and researcher access to online tools and services
Expand service across all disciplines working on small- to medium-sized gene sequencing projects through the Sequencing & Bioinformatics Consortium. Establish the Health Data Asset Inventory as an important resource, and increase the number of assets in the data set.
Status: Objective Met
The Sequencing & Bioinformatics Consortium has become established as a high-quality facility for small- to medium-sized gene sequencing projects on campus. It provides an excellent complement to other facilities in the area that serve much larger projects with a higher throughput model. The Consortium provides both sequencing services and scientific consultation on study design and analysis. The Health Data Asset Inventory has become established as an important resource, as have datasets related to equity and diversity metrics.
MANAGEMENT AND ADMINISTRATION
Increase the efficiency of the grant application and administration process by improving workflows for faculty and research personnel through new systems such as online clinical data sharing agreements and enhanced modules in the Researcher Information Services such as the Financial Status and Online Grant Submission Modules
Time required to develop and process grant applications and clinical data sharing agreements
Reduction in processing time and duration for the grant development, application and clinical data sharing cycle
Status: Objective Met
New efficiencies in the pre-award workflow for both grant and sponsored research have been possible because of the Research Support Fund. The creation of an online clinical data sharing agreement mechanism has significantly reduced processing times, with eligible projects now able to create a partially executed agreement immediately. In 2017/18 114 partially executed agreements were generated using this system.
REGULATORY REQUIREMENTS AND ACCREDITATION
Ensure UBC researchers meet all regulatory requirements in the most efficient manner by maintaining facilities, providing training, improving communications, and streamlining regulatory processes
Level of animal care training, findings on CCAC inspections, time to achieve full or conditional approval for animal or ethics protocols
Increase in the number of people trained in animal care and scholarly integrity. Increase visibility and content of the harmonized ACS and ACC websites. Zero “major” CCAC findings on inspection. Reduction in the time for animal and ethics protocols to be approved
Status: Objective Met
The Animal Care & Use Program continues to provide both mandatory and optional training opportunities to staff, researchers and students. Improvements have been made to the online presence of the Animal Care Committee and Animal Care Services to help enable better understanding and uptake of the various regulatory requirements. There were no “major” findings in the last CCAC visit. Cycle times for animal and human ethics review are stable; opportunities for further improvement relate to ongoing training around regulatory and policy requirements.
INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AND KNOWLEDGE MOBILIZATION
Through enhanced integration of the governance and operations of Innovation UBC, continue to provide internationally recognized level of service to researchers and external partners through the University-Industry Liaison Office, UBC Corporate Relations, and entrepreneurship @UBC
Knowledge mobilization metrics such as patenting, licensing, invention disclosures, spin-off company creation, venture participation in the entrepreneurship @UBC program, and industry partnerships created through the UILO and Corporate Relations
Maintain indicator performance levels, focus on increasing service levels to internal and external stakeholders. Launch new governance model and operational plan for Innovation UBC.
Status: Objective Met
Innovation UBC was launched with great success, and formalizes the connection between four pathways including knowledge exchange, partnership development, commercialization, and entrepreneurship. Applications to the entrepreneurship @UBC program remain stable, and domain expertise through the entrepreneur-in-residence program continues to strengthen. Service standards for patenting, licensing, and spin-off creation are stable, and opportunities to improve service standards are under active consideration.
FACILITIES
Increase the research capacity of UBC by renovating and/or and maintaining new and existing research facilities
Amount of significantly renovated research space
Increase efficiency, capacity and effectiveness of space utilization through reconfiguration of facilities such as the Advanced Research Computing (ARC) service and the Preclinical Discovery Centre
Reported Outcome: Target Met
The Preclinical Discovery Centre is scheduled for completion in 2017. This leading-edge facility is based at an academic health centre site, and is intended to replace an existing but out-of-date rodent-holding facility. With animals expected to occupy the facility this year, the capacity, efficiency and effectiveness of our animal care and use program will be significantly enhanced, particularly given its location at a teaching hospital.
The Research Support Fund also enabled the physical integration of the Advanced Research Computing team. This team had previously been distributed across UBC, and their now being co-located has immediately enhanced the efficiency and effectiveness of the high-performance computing and advanced research computing consulting services the team offers the UBC research enterprise.
RESOURCES
Increase access to research resources and performance data such as the Advanced Research Computing (ARC) service and by maintaining and expanding library resources and online tools such as SciVal and the UBC Research Metrics portal
Volume of library holdings and researcher access to online tools
Expand service across all disciplines working on questions that have large data and computational power needs through services such as ARC. Expand library holdings and increase the number of researchers accessing online research tools
Reported Outcome: Target Met
The Advanced Research Computing team has completed over 100 consultations, 38 data-research infrastructure presentations to internal and external stakeholders, 18 training sessions to over 450 attendees, and has over 150 participants registered for a high-performance computing Summer School. The University Data Centre has expanded, and new users are engaging with the Advanced Research Computing unit each month.
The University Library has implemented the first automated storage and retrieval system in Canada, and has a capacity of over 1,000,000 volumes.
The Research Metrics portal, a central, curated resource for senior administration, grant facilitators and others, now has almost 400 registered users. The number of users has been steadily increasing on a year-over-year basis. The portal presents data on research funding awarded to UBC, and is a resource for operational and strategic decision makers.
MANAGEMENT AND ADMINISTRATION
Increase the efficiency of the grant application and administration process by improving workflows for faculty and research personnel through new systems such as online Non-disclosure Agreements (NDA) and enhanced modules in the Researcher Information Services such as the Peer Review Module
Time required to develop and process grant applications and NDAs
Reduction in processing time and duration for the grant development, application and NDA cycle
Reported Outcome: Target Met
Improvements in the RISe system have focused on reducing turnaround time in the application and development cycle. Turnaround time in application processing has been improved through deployment of an onsite signatory at BC Children’s Hospital Institute. Further efficiencies will be realized in a new RISe workflow that enables paperless approval. Other improvements continue to be made that improve the efficiency of the entire review cycle. For example, a newly implemented pre-review feature allows certain types of deficiencies in applications to be addressed before the application is sent to the ACC or REB for review. The RSF will enable additional improvements to the RISe system in FY17/18. Business analysis is ongoing to assess and prioritize additional system efficiencies.
The University-Industry Liaison Office implemented an automated industry-friendly NDA web-portal. This resource allows UILO staff to focus on more complex agreements, while reducing the number of negotiated non-disclosure agreements by 40%.
REGULATORY REQUIREMENTS AND ACCREDITATION
Ensure UBC researchers meet all regulatory requirements in the most efficient manner by maintaining facilities, providing training, improving communications, and streamlining regulatory processes
Level of animal care training, scholarly integrity training, time to achieve full or conditional approval for animal or ethics protocols
Increase in the number of people trained in animal care and scholarly integrity. Increase visibility and content of the harmonized ACS and ACC websites. Reduction in the time for animal and ethics protocols to be approved
Reported Outcome: Target Met
In FY17, 820 students were trained in the animal care and use program, compared with 748 in FY16. With the benefit of the Research Support Fund, the Animal Care & Use Program (ACUP) has been able to improve the efficiency of a system for sharing sensitive policy and other documents. We are also using this resource as a repository for training materials, and as a communication pathway for users of UBC’s animal care facilities. The ACUP website has been refreshed to provide a much more engaging, easy-to-navigate and comprehensive resource for people wanting to learn about the Program. The site now houses guides to help researchers navigate the process from funding and proposal development through to knowledge translation, guidelines on general rodent care and procedures, and information about the University’s training requirements for animal handling and protocol writing.
Applications to the Animal Care Committee (ACC) are now automated in the University’s RISe system, and we have already seen a decrease in cycle time for applications to the ACC as a result of this change.
INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AND KNOWLEDGE MOBILIZATION
Continue to provide internationally recognized level of service to researchers and external partners by supporting the activities of offices and initiatives such as the University-Industry Liaison Office, entrepreneurship@ UBC and the Innovation Office
Knowledge mobilization metrics such as patenting, licensing, invention disclosures, spin-off company creation, venture participation in the entrepreneurship@ UBC program, and industry partnerships created through the Innovation Office
Maintain indicator performance levels, focus on increasing service levels to internal and external stakeholders
Reported Outcome: Target Met
During fiscal year 2017 the number of technology disclosures received by the UILO remained steady at 154. A total of 154 patents were filed in FY2017, down from the previous year, but commercialization agreements increased to 122 (encompassing licenses, assignments, term sheets and options). In FY16 the number of spin-off companies based on UBC intellectual property rose to 13 from 8 in FY15, and rose again in FY17 to 15. The RSF helped enable a new automated, industry-friendly NDA web-portal in order to re-allocate staff time on to higher value contracts. As a result, the number of negotiated NDA decreased 40%. 1,326 industry-based research contracts were carried out in 2017, with a combined budget value 11% higher than in FY16.
FACILITIES
Increase the research capacity of UBC by renovating and/or and maintaining new and existing research facilities
Amount of significantly renovated research space
Increase efficiency, capacity and effectiveness of space utilization through reconfiguration of facilities such as the Centre for Disease Modelling
Reported Outcome: Target Met
In 2015, the Centre for Disease Modelling (CDM) underwent a major renovation and reconfiguration. This facility houses mouse and rat facilities, and was expanded to accommodate animals from another facility on campus that was being decommissioned. Upgrades to the facility – that will allow a broader range of research activity – included improved vibration and sound control, elimination of airlocks creating safer and more efficient transport of supplies, and improved physical barriers between breeding and other zones within the facility.
Other more general upgrades included an improved air filtration and HVAC systems, new autoclaving and laundry systems, an expansion of the network to transport oxygen and carbon dioxide which are now available to more procedure rooms within the facility, and installation of additional drains in the cage processing rooms, allowing for more efficient operations and reduced downtime for reusable assets. Existing assets including a DEXA scanner and gamma irradiator were moved to other parts of the CDM facility to allow greater access and improved efficiency.
The renovation also saw improvements in staff facilities, including enhancements to locker rooms, office space, and other common areas.
RESOURCES
Increase access to research resources and performance data by maintaining and expanding library resources and online tools such as SciVal and the UBC Research Metrics portal
Volume of library holdings and researcher access to online tools
Expand library holdings and increase the number of researchers accessing online research tools
Reported Outcome: Target Met
In the 2015-2016 fiscal year, the Library saw an increase in the use of all library e-resources since the previous year. In particular, ebook section downloads increased over 40% from previous year. In 2014-2015, the section downloads were 5,223,874. In 2015-2016, the section downloads increased to 7,308,647, representing an increase of 2,084773 downloads.
Ejournal article downloads increased 11% over the same time period. In 2014-2015, article downloads were 7,115,728. In 2015-2016, the article downloads increased 805,399 for a total of 7,921,127.
In addition, Library holdings (electronic and physical) were increased in several areas. The increases were not as great as compared to previous years as a result of the collections budget situation.
|
FY 2014/15 |
FY 2015/16 |
Change |
% change |
|
|
Unique eBook titles |
1,894,548 |
2,102,033 |
207,485 |
11% |
|
Unique eJournal titles |
371,752 |
392,329 |
20,577 |
6% |
|
Physical items |
4,955,122 |
4,999,993 |
44,871 |
1% |
A decision was made to acquire access to the SciVal platform through the Office of Research Services rather than the library. The UBC Research Metrics portal is managed through the VPRI Office, and was expanded to include data on international partnerships.
The University is assisting the Library this year (2016-2017) with a lift to the collections budget of $2 million dollars. $300,000 of the $2 million lift will be a permanent addition to the collections budget. With this assistance the Library is able to renew the vast majority of the serial and databases subscriptions this year as well as restart the Library monographic approval plans. Without the assistance this would not have been possible. In fiscal year 2015-2016, the University assisted the library with a one -time $600,000 dollar lift.
MANAGEMENT AND ADMINISTRATION
Increase the efficiency of the grant application process by improving workflows for faculty and research personnel through new systems such as enhanced modules in the Researcher Information Services and implementing WorkZone within support offices
Time required to develop and process grant applications
Reduction in processing time and duration for grant development and application
Reported Outcome: Target Met
In FY16 research funding at UBC increased by 13% from $530 million to $599 million compared to the past year. Total number of funded projects also increased by 6% from 8,278 to 8,766. Numbers of new, peer-reviewed projects, showed a significant increase of 16% from 3,560 to 4,142 over the year. Review and approval time for applications approved by the university remained constant despite the increased volume. Review and processing time from the time of award to issuance of account details decreased by one day from 13 to 12 days.
Workflows were streamlined in the Researcher Information Services (RISe) system with enhanced modules in research funding reporting as well as a new peer review module. Improvements to the existing Extended Reporting module made self-service reporting for the faculties and departments easier. To leverage improved technology upgrades to the RISe new reporting tools are being evaluated with the goal of enhancing and expanding current reporting capabilities. The new peer review module for animal care was successfully deployed allowing secure and streamlined review of protocols within RISe as well as automated workflow to handle routing of documents through the review processes.
Project management software WorkZone was implemented in the ORS in 2015/16. This package provides strategic research funding development services designed to develop capacity and build collaborations. Implementing WorkZone is still in process and is being evaluated as it, and other project management systems, are being assessed for suitability to meet the needs of the entire group.
REGULATORY REQUIREMENTS AND ACCREDITATION
Ensure UBC researchers meet all regulatory requirements in the most efficient manner by maintaining facilities, providing training and streamlining regulatory processes
Level of animal care training, time to achieve full or conditional approval for animal or ethics protocols
Increase in the number of people trained in animal care, reduction in the time for animal and ethics protocols to be approved
Reported Outcome: Target Met
The average cycle time from protocol submission to approval is 42 days. Since the introduction of pre-review and conditional approval, a large percentage of protocols are approved outright. Conditional approval is given when protocols are missing information that does not affect animal welfare.
The animal care training program at UBC was re-engineered to include a significant amount of hands on training and score participants based on their competency and proficiency, as opposed to being evaluated on a simple pass/fail basis. The training program is made up of online modules including the Canadian Council on Animal Care (CCAC) ethics course, and practical components. The number of participants in this training program has increased yearly:
|
Course |
# Researchers: 2013 |
# Researchers: 2015 |
|
Introduction to Working with Rodents in Research |
140 |
319 |
|
Rodent Anesthesia |
78 |
139 |
|
Rodent Surgery |
105 |
67 |
|
Workshops |
48 |
191 |
We believe this enhanced training has resulted in the reduction in the number of any non-compliance issues that has been observed since the revised approach was implemented.
INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AND KNOWLEDGE MOBILIZATION
Continue to provide internationally recognized level of service to researchers and external partners by supporting the activities of offices and initiatives such as the University-Industry Liaison Office and entrepreneurship@ UBC
Knowledge mobilization metrics such as patenting, licensing, invention disclosures, spin-off company creation and participation in the entrepreneurship@ UBC program
Maintain service levels, increase spin-off company creation, increase participation in entrepreneurship@ UBC
Reported Outcome: Target Met
Thirteen spin-off companies were created by UBC faculty, staff and students in 2015/16, 5 more than in 2014/15. Since 1984, UBC and the UILO have supported the creation of 182 spin-off companies. This puts UBC in the 92nd percentile among North American universities and the 97th percentile for Canadian universities for start-up activity. The 61 start-ups formed from licensed UBC technology between 2005 and 2015 have together raised greater than $540 million in capital and employ more than 400 people.
The UILO’s Sponsored Research Group leads Canadian universities in contract negotiation, having negotiated 2,523 contracts in 2015/16, accounting for $142.6M in research funding. The number of contracts negotiated has been increasing by approximately 8% every year over the last decade, while the time to negotiate those contracts is steadily being reduced.
The e @ UBC program created numerous opportunities for participation in entrepreneurship activity throughout the pathway from idea to funding. Two sector-specific activity tracks were created – one in the life sciences and one in impact (social / environmental) ventures to reflect specific entrepreneurial potential on campus. Increased participation was seen in activities across the idea-to-funding process funnel; notable examples include consistent attendance at weekly orientation sessions, and more than 120 attendees at so-called Startup Weekends, which are concentrated, sector-specific opportunities for teams to develop business ideas and hypotheses. A new lecture series on venture creation topics was very well attended, as was a venture showcase event which exposed high potential ventures to an external business and financial audience. Other collaborative initiatives engaged stakeholders from key Faculties to develop and promote entrepreneurship at UBC.
Facilities
UBC’s average building age is approximately 35 years old, and deteriorating laboratories have to be improved to comply with current codes and to meet changing demands in order to attract and retain world-class investigators.
RSF funds at UBC mitigate deferred maintenance, cover operating costs and help provide valuable technical support for our laboratories, helping to provide an optimal lifecycle for our buildings.
Specific examples of RSF support for facilities include:
- The renovation of the Robert H.N. Ho Research Centre atrium space located at the Vancouver General Hospital campus. The new space will support advanced cross-disciplinary researchers from the Centre for Hip Health and Mobility, OvCare and the Vancouver Prostate Centre.
- The replacement of vital components for research and communications systems and the renewal of important maintenance contracts
- The occupancy costs of new buildings such as the Centre of Brain Health
- Support of the WestGrid for UBC Information Technology
Resources
RSF funding supported multiple resources at UBC, including the UBC Library.
In the past year UBC Libraries has, through subscriptions, provided online access to:
- More than 1.8 million e-books; usage exceeds 3.9 million annually
- More 331,000 e-journals (tripled since three years ago); usage exceeds 7.6 million article downloads
- More than 2,000 bibliographic and full text databases
- More than 500,000 locally produced digital items
UBC Libraries physical collections include:
- More than 7.4 million items in the collection
- Nearly 877,599 maps, audio, video and graphic materials
- More than 5.3 million microforms
UBC also provided access to Springers' ebooks and ejournals.
Management + Administration
Expenditures pertaining to the management and administration of UBC’s research enterprise represent the largest portion of our RSF grant funding. Without these key personnel the research performance at UBC would be significantly impaired. Examples of RSF funded support include:
- UBC is exploring mechanisms such as shared research systems to increase the efficiency and decrease costs in BC.
- Many of UBC’s faculties and affiliated institutions hire dedicated staff to assist with research and grant facilitation and planning.
- RSF funds also support the planning and promotion of research at UBC
Regulatory Requirements + Accreditation
RSF Funds have supported activities to ensure the health and safety of UBC researchers, and to enable them to pursue world-class research in facilities found only in premier institutions. Some examples of RSF fund allocation include:
- UBC’s affiliated Research Ethics Boards (REBs) oversee more than 7,000 research studies involving humans annually
- An internal audit of our processes was conducted for ensuring compliance with US Federal Government enacted regulations pertaining to Financial Conflict of Interest requirements
- RSF funds contributed to UBC’s continuing efforts to assist with provincial harmonization of multi-jurisdictional studies in BC.
- Continual review and approval to ensure appropriate safe handling, use, and disposal of infectious agents and hazardous materials.
- An effective Occupational Research Health and Safety Program, including an ever-expanding Biosafety Program, Chemical Safety program, and a Radiation Safety program
Intellectual Property
As the first Canadian office of its kind, the UBC University Industry Liaison Office (UILO) exemplifies the pioneering and entrepreneurial spirit of UBC, and the University has become a recognized international leader for its commercialization activities.
Funding from the Research Support Fund has provided critical value-added support for several key positions and activities within the UILO. Through the salary support of key staff in the UILO office, the Research Support Fund is core to the success of technology transfer operations and has allowed the development and support of successful new initiatives such as the UILO start-up services voucher program, knowledge mobilization initiatives and the Global Access Initiative.
RSF funding has been used to support patent applications and to provide salary support for multiple positions within the UILO.